Each nucleotide is made up of three components. The process of protein production involves two steps.

Nucleic Acids Study Guide Inspirit
RNA functions primarily in the cytoplasm of the cell as a template in connection with the synthesis of proteins as well as in the ribosomes.
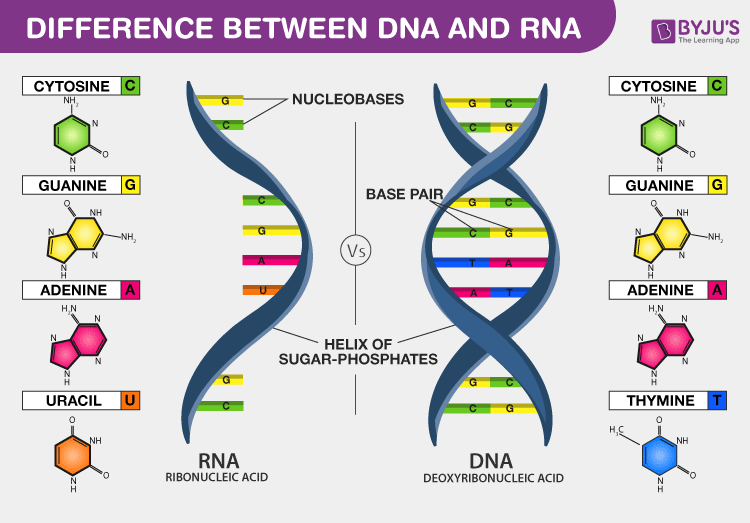
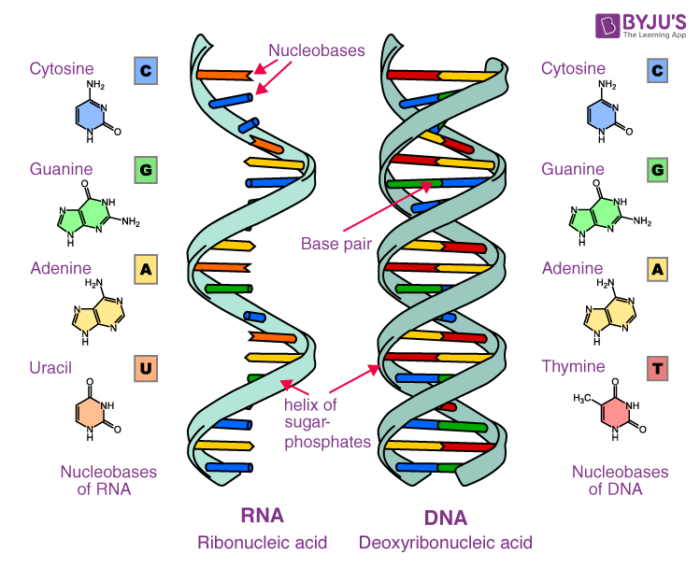
. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA encodes the information cells need to make proteins. Dna has deoxyribose and rna has ribose dna is double stranded and rna is single. The RNA molecule is also composed of phosphoric acid a pentose sugar and some cyclic bases.
Lesson summary the role of rna rna ribonucleic acid is a nucleic. All the information of a cell is stored in DNA. The functions performed by these are as follows.
Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. The two principal nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. 13 1 rna worksheet answers.
They store all the pieces of information related to life and control almost all of the life activities of the cell directly or indirectly. Nucleic acids are made up of strands of nucleotides which are made up of a base containing nitrogen called a nitrogenous base a sugar that contains five-carbon molecules and a phosphoric acid. Functions of Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acid is responsible for the synthesis of protein in our body RNA is a vital component of protein synthesis.
Compare and contrast the structural components of DNA and RNA. DNA which stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA which stands for ribonucleic acid. In RNA the nucleotide bases are ribose and the common pyrimidine bases are uracil and cytosine.
DNA is an essential component required for transferring genes from parents to offspring. Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are macromolecules that store genetic information and enable protein production. Describe the roles of nucleic acids in storing and transmitting biological information.
Gene expression is the way in. DNA and RNA is shared under a not declared license and was authored remixed andor. The central dogma of molecular biology is that information is transferred from dna to rna to protein.
There are two types of nucleic acid. Chemically DNA is composed of a pentose sugar phosphoric acid and some cyclic bases. It creates DNA and RNA which store the information needed by cells to create proteins.
Explain how ionizing radiation may cause genetic mutations in human and animal DNA and may cause some forms of cancer. This information is stored in multiple sets of. Sponk DNA is a double-stranded molecule organized into chromosome found in the nucleus of cells where it encodes the genetic information of an organism.
This intermediary is the messenger RNA mRNA. They are both linear polymers consisting of sugars phosphates and bases but there are some key differences which separate the two 1. These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides.
Nucleic Acids - Classification Function of Nucleic Acids Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. A related type of nucleic acid called ribonucleic acid RNA comes in different molecular forms that play multiple cellular roles including protein synthesis.
The second-from-the-right nucleotide from DNA is replaced by a C. Molecular structure of DNA. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell.
MRNA rRNA tRNA miRNA and siRNA. 4 RNA function is to interpret the code in DNA and direct synthesis of proteins gene an information containing segment if DNA that codes for the production of a molecule of RNA which in most cases goes on to play a role in protein synthesis. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids found in the cells of living organisms.
A major function of nucleic acids involves the storage and expression of genomic information. 26 Radiation can be very damaging to the human body. _____ _____ name 2 pyrimidines.
There are two types of nucleic acids. DNA and RNA in Cells DNA and RNA Comparison. Ribonucleic Acid Ribonucleic acid occurs chiefly in the.
What are two types of nucleic acids. In DNA the nucleotides contain 2-deoxyribose and the common pyrimidine bases are thymine and cytosine. From 84 Identify other key functions of nucleotides including their roles as.
Nucleic acids help synthesize proteins in the body. Carriers of chemical energy in cells Components of many enzyme cofactors Regulatory. DNA controls all of the cellular activities by turning the genes on or off The other type of nucleic acid RNA is mostly involved in protein synthesis.
A nitrogenous base a pentose five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group Figure 52Each nitrogenous base in a nucleotide is attached to a sugar molecule which is attached to one or. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology responsible for the storage and reading of genetic information that underpins all life. A nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems.
RNA is an especially important factor in the manufacturing of proteins. Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base a five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group.
Introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. The DNA molecules never leave the nucleus but instead use an intermediary to communicate with the rest of the cell. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA carries the sequence of coded instructions for the synthesis of proteins which are transcribed into ribonucleic acid RNA to be further translated into actual proteins.
The primary purines are adenine and guanine in both RNA and DNA. The sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA is oppositeNucleic acids mainly DNA and RNA play an essential role in the bodies of living organisms. DNA produces a messenger RNA mRNA which helps in placing amino acids in the code for protein synthesis.
DNA is responsible for the synthesis of RNA. Loss of DNA content is linked to many diseases. DNA and RNA are made up of monomers known as nucleotidesThe nucleotides combine with each other to form a nucleic acid DNA or RNA.
DNA and RNA structure and function. Molecular structure of RNA.

Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna
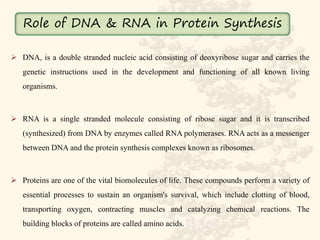
Role Of Dna And Rna In Protein Synthesis
Nucleic Acids Definition Examples Functions Of Nucleic Acids

0 Comments