What is the ultimate goalpurpose of mitosis. The human body is composed of trillions of cells.
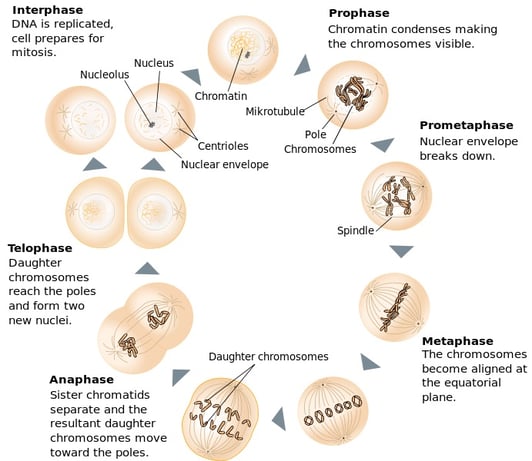
The 4 Mitosis Phases Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
The goal of mitosis is to multiply the cells.

. The two types of cells are. Cells can be color coded display text numbers and the. They are usually found in unicellular organisms which are referred to as prokaryotes.
Why Do Cells Divide. A sperm cell is a gamete zygote and is a haploid diploid gamete haploid. Thus we can understand why cells are known as the structural and functional unit of life.
Enough -cytosis for you. A single cell divides to make two cells and these two cells then divide to make four cells and so on. Male sex cells or sperm are motile and have long tail-like projections called flagella.
Any data that you want to enter into your worksheet must be placed in a cell. Cells also contain the bodys hereditary material and can make copies of themselves. Human beings are made up of more than 75 trillion cells.
When a sperm cell and ovumegg merge they undergo the process of fertilization and give rise to a gamete zygote which is haploid diploid zygote diploid. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. On occasion a distinction in terms is made between a G0 cell and a quiescent cell eg heart muscle cells and neurons which will never enter the G1 phase whereas other G0 cells may.
A disease caused by abnormal cells in the body. We call this process cell division and cell reproduction because new cells are formed when old cells divide. Cell A cell is a rectangle or block housed in a worksheet.
Because most cells are too small to be seen by the naked eye the study of cells has depended heavily on the use of microscopes. A disease caused by abnormal cells in the body. What term do we use to describe the new cells.
Prokaryotic cells These cells lack a well-organised nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. Cell cycle is the name we give the process through which cells replicate and make two new cells.
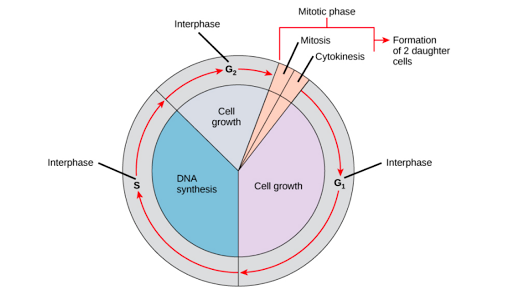
Exocytosis is the general term for cell release endocytosis is the general term for cell consumption and pinocytosis and phagocytosis are specific types of endocytosis. Cell cycle has different stages called G1 S G2 and M. Indeed the very discovery of cells arose from the development of the microscope.
The cell is the smallest unit with the basic properties of life. The study of cells is. In this article we explain some of the structures found in cells and describe a.
Cell biology is the study of cells their physiology structure and life cycle. Somatic cell nuclear transfer SCNT technique in which the nucleus of a somatic body cell is transferred to the cytoplasm of an enucleated egg an egg that has had its own nucleus removed. Every organism or living thing is made up of structures called cells.
Once inside the egg the somatic nucleus is reprogrammed by egg cytoplasmic factors to become a zygote fertilized egg nucleus. These daughter cells become either new stem cells or specialized cells differentiation with a more specific function such as blood cells brain cells heart muscle cells or bone cells. The cells fo the skin and digestive tract and cells in the bone marrow that make blood cells grow and divide rapidly throughout life.
Blast- relates to immature cells -oma means tumour. Cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all living organisms and is a membrane bound structure enclosing the protoplasm. Read more changes when a formula is copied or dragged to another cell.
The ability of cells to divide is unique for living organisms. Some tiny organisms such as bacteria and yeast consist of only one cell. It makes it possible for asexual reproduction and ordinary cell division in living things to happen.
Answer an application question on the life spans of human cells. To do this it then moves into the S phase where the cell copies all the DNA. Meiosis causes the daughter cells to be genetically different from the parent cells.
The new cells are called daughter cells. When cells divide they make new cells. Humans are made up of trillions of cells the basic unit of life on earth.
Lets say we have B1C1 in cell A1 and we copy this formula to cell B2 and it becomes C2D2. What is a cell. G1 is the stage where the cell is preparing to divide.
Sex cells or gametes are reproductive cells created in male and female gonads that bring new life into existence. So S stands for DNA synthesis. Enough -cytosis for you.
Relative cell reference type in excel Relative Cell Reference Type In Excel In Excel relative references are a type of cell reference that changes when the same formula is copied to different cells or worksheets. They provide structure for the body take in nutrients from food convert those nutrients into energy and carry out specialized functions. 27 rows A Sperm cell is a gamete zygote and is haploid diploid.
In the human body most muscle cells and nerve cells do not divide at all once they have developed. Osteo-means bone -genic means creating causing Thus we can see that this is a bone forming tumour. To take another type of tumour.
Therefore by breaking down a complex word we can see that neuroblastoma literally means a tumour made up of immature nerve cells. A cell aids in reproduction through the processes called mitosis and meiosis. Robert Hooke first coined the term cell following his observations of a piece of cork with a simple light microscope in 1665.
Mitosis is termed as the asexual reproduction where the parent cell divides to form daughter cells. All living organisms are composed of cells from just one unicellular to many trillions multicellular. A cell is the smallest unit that is typically considered alive and is a fundamental unit of life.
The process by which a cell divides into two smaller cells that each contain the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. Large plants and animals have many billions of cells.

Meiosis Definition Stages Function And Purpose Biology Dictionary Meiosis Biology Cell Biology

Mitosis And Cytokinesis Human Anatomy And Physiology Biology Notes Anatomy And Physiology

Mitosis Vs Meiosis Key Differences Chart And Venn Diagram Technology Networks

Mitotic Figure Pathology Dictionary Mypathologyreport Ca

10 Key Differences Between Mitosis And Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis Vs Meiosis

Difference Between Plasmolysis And Deplasmolysis Definition Mechanism Result And Differences Biology Notes Cell Wall Cell Membrane

Mobile Network Thoroughly Explained A New Cell Phone Newest Cell Phones Networking Cell

0 Comments